On the Nose: Scientists Optimize Intranasal Anti-Depressant Drug Delivery to the Brain
Japanese researchers have succeeded in effective intranasal delivery of modified anti-depressant peptide-based drug to the brain
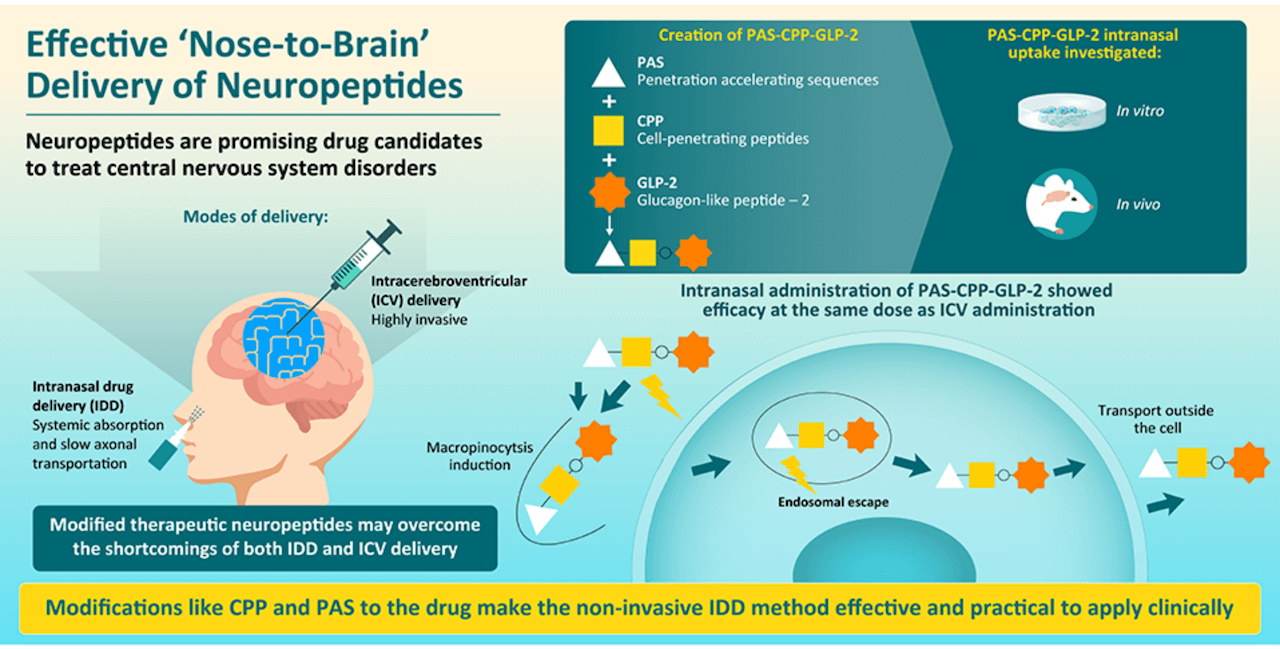
Drug delivery to the brain has been challenging, owing to disadvantages like systemic absorption, slow axonal transportation, rapid drug degradation, and invasiveness of commonly used techniques. Accordingly, researchers from Japan have successfully attempted to bolster intranasal drug delivery to the brain, making it as effective as other conventional delivery methods, by adding sequences that enhance cell permeability and degradation escape to an anti-depressant drug called glucagon-like peptide 2. Their findings are published in the Journal of Controlled Release.
More;
https://www.tus.ac.jp/en/mediarelations/archive/20211111_8305.html
مطالب مرتبط

نشست دفاع از پایان نامه
۳ / مهر / ۱۴۰۳

انتشار نسخه جدید فصلنامه تازههای علوم شناختی: دوره ۲۵، شماره ۲
۱۵ / آبان / ۱۴۰۲